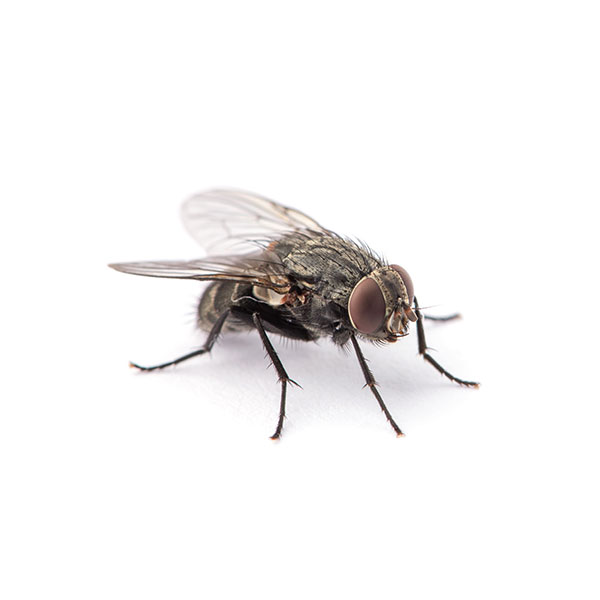
House Flies in San Angelo
The house fly, found on every continent except Antarctica, is one of the most well-known insects. During the hotter summer months, house flies are commonly found in large numbers and tend to reside near humans and animals. They prefer breeding in places like animal wastes and decaying organic matter, including animal remains and discarded food waste. In these environments, they can pick up bacteria and viruses that have the potential to cause human disease.
One of the significant concerns with house flies is their habit of defecating almost every time they land. This behavior contaminates food and surfaces, posing a risk of disease transmission. Proper pest control measures and good hygiene practices are essential in minimizing the impact of house flies and reducing the risk of disease spread in areas where humans and animals coexist.
House Fly Habitat
In rural settings, house flies often originate from manure piles, while in urban areas, large numbers of flies are commonly generated from piles of fermenting lawn clippings. Flies are particularly attracted to animal manure, and the most significant breeding sites include horse manure, human excrement, cow manure, fermenting vegetable waste, dumpsters, refuse containers, and household garbage. Certain fly species can even live and breed in recycling containers, making fly issues common in recycling centers. Proper waste management and sanitation practices are crucial in controlling fly populations and preventing potential health risks associated with their presence.
House Fly Behaviors, Threats, or Dangers
House flies may not bite, but they possess the ability to transfer over 100 different pathogens, including salmonellosis, typhoid, and tuberculosis. These disease-causing organisms are acquired by flies from sources of filth like garbage, sewage, and other unclean environments. The pathogens are then transmitted from the flies’ mouthparts, vomit, feces, and contaminated body parts to human and animal food.
House flies act as vectors, carrying a diverse range of germs from their breeding sites to our dinner tables, or even spreading diseases within animal herds or flocks. Proper sanitation practices and preventive measures are crucial in minimizing the risk of disease transmission from house flies and ensuring the safety of food and living environments. If you are experiencing a house fly infestation on your property, contact your local fly exterminators for help.